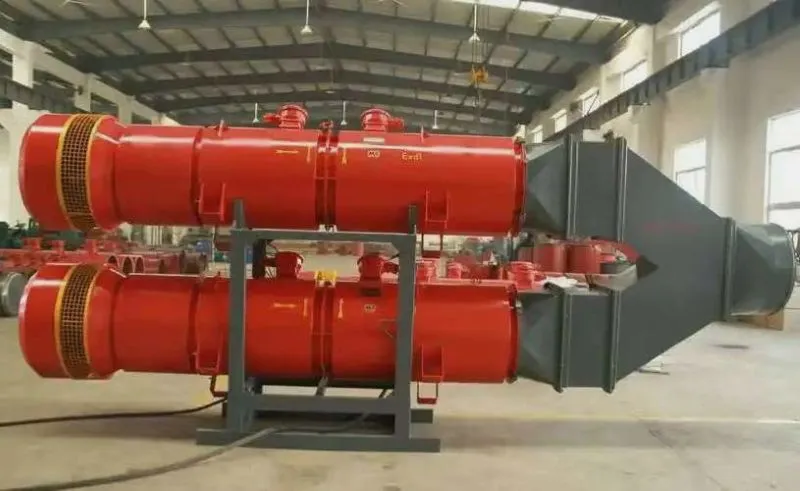
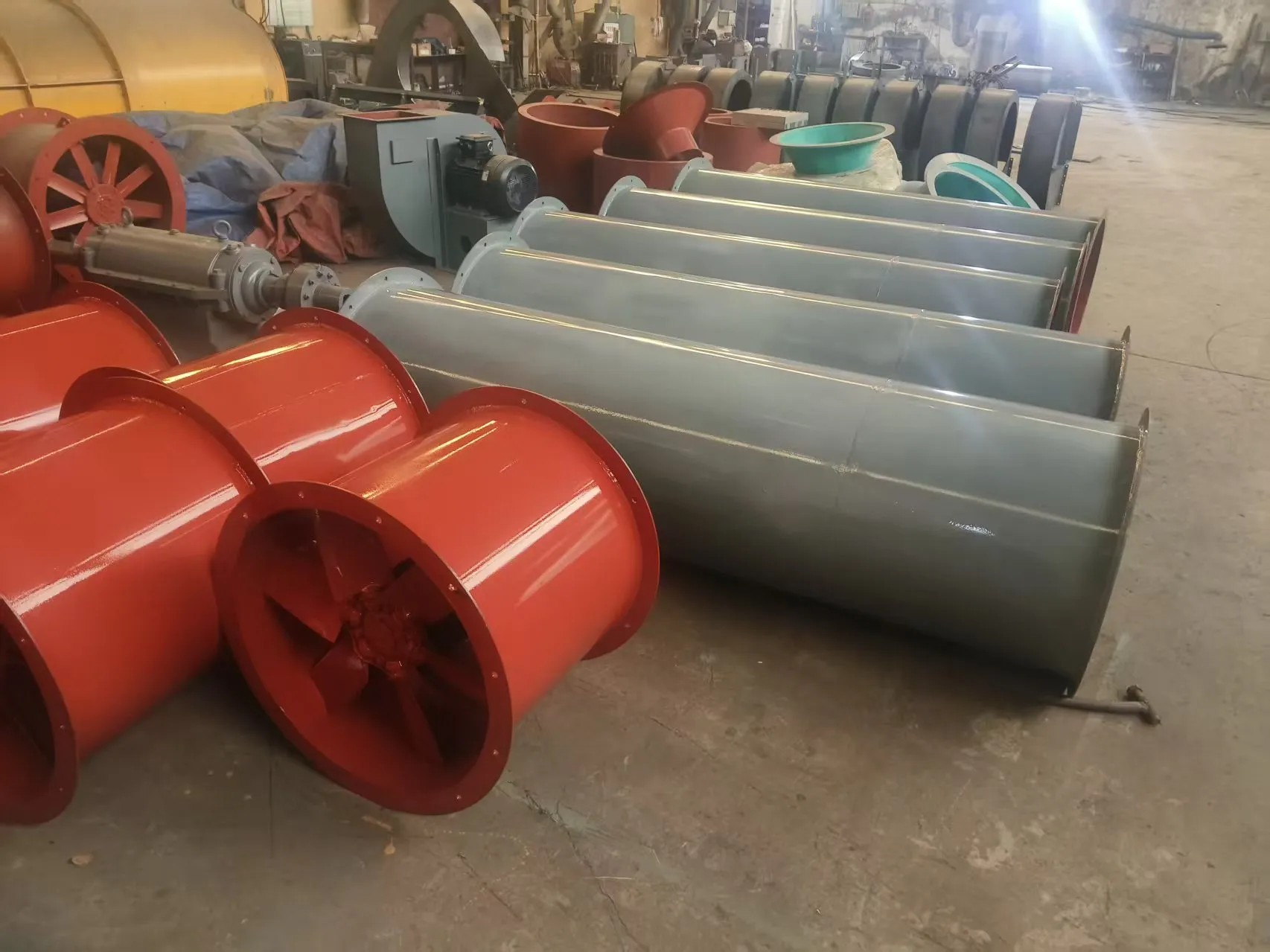
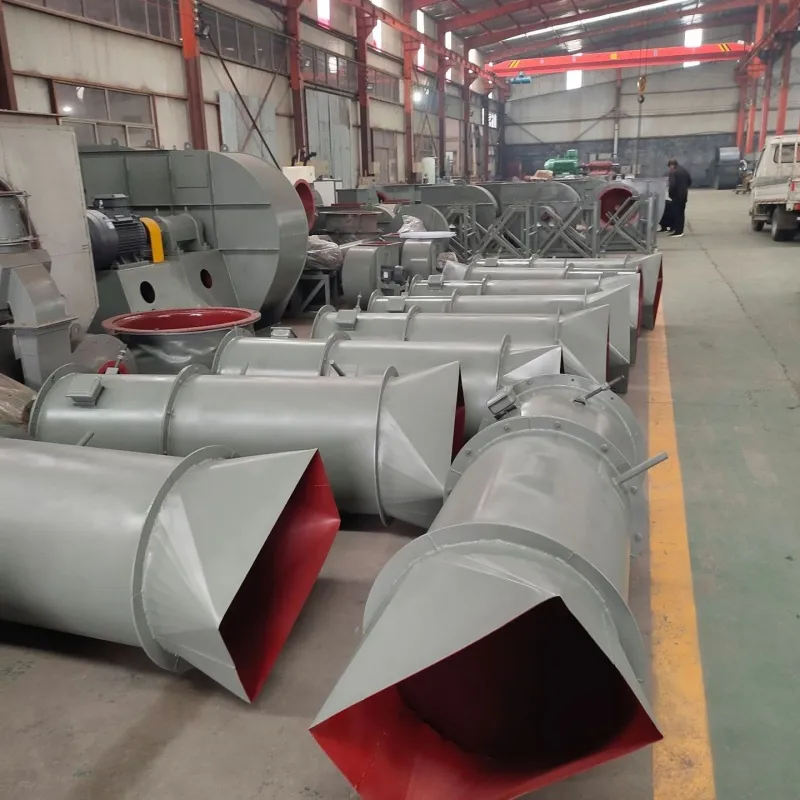
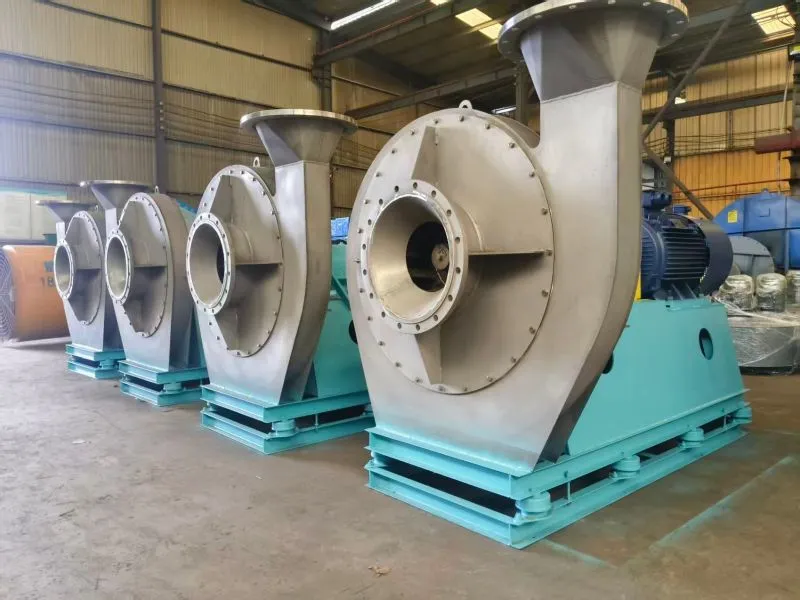
Cement plant kiln heat dissipation fan post type axial flow fan in cement plant kilns are mainly classified based on the application scenarios and functional requirements. The common types include the following:
1. General ventilation and air exchange type
This is the most basic application form of the T30 axial flow fan, mainly used for air replacement in enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces such as factories, workshops, warehouses, and basements. By forcing air circulation, it can expel the stale air (such as dust, odors, and hot and humid air) in the room and introduce fresh air, improving indoor air quality and ensuring the comfort of personnel and the safety of the production environment. For example, it is suitable for scenarios such as expelling metal dust in mechanical processing workshops and dispersing hot and humid air in textile workshops.
2. Positional air supply / cooling type
Designed to meet the local cooling or air supply needs of specific work positions within the workshop (such as welding stations, assembly operation tables, and areas near high-temperature equipment). It is usually used in conjunction with a mobile stand and can be moved to the target position to directly supply air to the operator, reducing the local environmental temperature and dispersing harmful gases (such as welding fumes), enhancing the comfort of the job position, and preventing operators from being exposed to high temperatures or poor air quality for long periods.
3. Pipeline exhaust / air supply type
Some T30 axial flow fans can be adapted to pipeline systems and used as duct fans. By connecting to air ducts, they can achieve directional exhaust or air supply in specific areas, such as local exhaust systems in buildings (such as bathrooms and kitchen auxiliary exhaust) and air flow transportation between processes on production lines (such as material cooling air flow transportation in the light industry). These fans need to match the pipe size to ensure that the air pressure can overcome the resistance of the pipeline.
4. Auxiliary cooling
Used for auxiliary cooling of industrial equipment, electrical cabinets, and small refrigeration units, etc. For example, a T30 fan placed beside the motor housing can accelerate the cooling of the motor, preventing equipment damage due to overheating from long-term operation; a small T30 fan inside an electrical cabinet can expel the heat generated by electrical components, ensuring the stable operation of the circuit.
5. Temporary emergency ventilation type
The T30 fan with a mobile stand can be used as an emergency ventilation device for sudden situations (such as temporary maintenance of factories, ventilation and drying after basement flooding, and dispersion of harmful gases at accident sites). Its portable feature enables quick response to temporary ventilation needs, compensating for the shortcomings of fixed ventilation systems.
The T30 axial flow fan is a widely used general-purpose axial ventilation equipment. With its compact structure and stable operation, it can meet the ventilation and air exchange needs of various scenarios. The following is a detailed introduction from the aspects of core parameters, structural design, derivative models, and installation and maintenance:
1. Core Performance Parameters
Specifications and Air Volume and Pressure: This fan series is rich in variety, with a total of 46 models. The number of blades includes 3, 4, 6, 8, and 9 types. The model numbers range from No. 2.5 to No. 10 (No. 2.5 is unique to the 4-blade type, while the rest of the blade types have model numbers from No. 3 to No. 10). The air volume range is 550 – 49,500 m³/h, and the pressure range is 25 – 505 Pa, which can meet the ventilation requirements of different spaces.
Speed and Power: Models No. 3 to No. 8 are available in two motor speeds, while No. 9 and No. 10 have only one speed. The motor power varies with the model number and operating conditions. For small models like No. 2.5, the power is as low as 0.09 kW, and for large models like No. 10, the power can reach 11.0 kW, which can match the power requirements for different air volumes and pressures.
Operating Conditions: It is only suitable for conveying non-corrosive and non-significantly dusty gases, and the gas temperature must not exceed 80°C to avoid component damage and affect the equipment’s lifespan.
2. Structural Design
The fan consists of a motor, a wind tube, an impeller, a bracket, and a protective net.
Impeller: Composed of blades and a hub, the blades are formed by stamping thin steel plates and welded to the outer circle of the hub. Different blade numbers correspond to different installation angles. For 3-blade types, the angles are 10°, 15°, etc., and for 4, 6, and 8-blade types, the angles are 15°, 20°, etc. Angle adjustment can adapt to different air volume requirements. The impeller is directly connected to the motor shaft, ensuring high transmission efficiency.
Casing: It includes a wind tube and a base frame. The base frame is made of thin steel plates or profiles, which can protect the internal components and achieve stable installation through the base frame, suitable for both fixed and mobile installation scenarios.
Protective Net: Prevents leaves and other debris from entering the wind tube and damaging the impeller.
Motor: It is a YE3 energy-saving copper core motor.
3. Derivative Models
The main derivative model is the BT30 explosion-proof axial flow fan. Its impeller (excluding the shaft disk) is made of aluminum, and it is equipped with an explosion-proof motor. The switch is either an explosion-proof switch or installed away from explosive areas. This model is suitable for industries such as chemical engineering and pharmaceuticals and can be used to exhaust flammable non-volatile gases. The installation process is the same as that of the ordinary T30 axial flow fan, and its safety meets the explosion-proof requirements of special industries.
Cement plant kiln heat dissipation fan post type


I. Core Safety Operation Principles
– Before operation, it is essential to ensure personal protection is in place. Wear insulated gloves and anti-slip work shoes. Long hair must be tied up. Loose clothing or jewelry is strictly prohibited to prevent entanglement in rotating parts.
Before starting up, the operation area must be cleared, and a warning sign reading “Equipment starting up, no entry” should be set up to ensure that irrelevant personnel evacuate to a safe area, preventing injuries caused by air flow impact or component detachment.
All operations must be carried out by certified personnel who have received specialized training. Non-professionals are strictly prohibited from touching the control cabinet switches, motor wiring, and rotating parts of the fan. During maintenance, the “power off – tag – lock” procedure must be strictly followed.
In case of any emergency during the startup process (such as unauthorized personnel entering or loud abnormal noises from the equipment), immediately press the “Emergency Stop” button on the control cabinet to cut off the power supply, and then proceed with subsequent handling. It is strictly prohibited to directly interfere with the equipment while it is in operation.
II. Special Precautions for Startup Operations
The axial flow fan is designed with a “no-load start” feature. A closed air duct will cause a sudden increase in air flow resistance, leading to motor overload and tripping. If this persists for a long time, it will burn out the motor windings.
Do not start under conditions of phase loss or abnormal voltage. Before starting, it is necessary to check the three-phase voltage with a multimeter to ensure it matches the rated voltage of the motor, and the three-phase imbalance should not exceed 2%.
The rotation direction of the fan impeller must be consistent with the direction of the arrow on the fan housing.
The interval between two consecutive starts of the same fan must not be shortened. For fans with a power of ≤15kW, the interval should be no less than 10 minutes; for those with a power of >15kW, the interval should be no less than 15 minutes. This is to prevent insulation aging caused by residual heat in the motor windings not dissipating. The bearings of the fan motor are maintenance-free.
It is strictly prohibited to start the equipment without conducting a mechanical inspection before startup. Do not start the device until the impeller has been manually turned to confirm its flexibility, to prevent bearing burnout or impeller damage due to jamming or lack of oil.
Do not force start under adverse conditions. In thunderstorm weather, when outdoor fans encounter strong winds (wind speed > 10m/s), or when the concentration of dust/corrosive gases exceeds the standard, starting should be stopped to prevent equipment failure or safety accidents.
III. Key Requirements for Operation Monitoring
The first 15 minutes after startup is a critical monitoring period. During this time, the motor current, bearing temperature and vibration values should be recorded every 5 minutes. The current should be stable within ±10% of the rated value, the bearing temperature should not exceed 75℃, and the vibration value should not exceed 4.5mm/s (specific values are subject to the equipment manual).
Real-time monitoring of the operating sound of the equipment is necessary. The normal sound should be a steady “hum”. If sharp abnormal sounds, periodic impact sounds or friction sounds occur, the machine must be stopped immediately for inspection to rule out problems such as impeller rubbing against the casing or abnormal sounds from the motor bearings.
Keep a close watch on the instruments and indicator lights on the control cabinet. If faults such as “overcurrent”, “overtemperature”, or “phase loss” are reported, stop the machine immediately. Only after the faults are eliminated and the alarms reset can the machine be restarted. It is strictly forbidden to operate with faults.
IV. Notes on Equipment Maintenance and Its Correlations
Before starting every day, the protective net at the air inlet of the fan and the surrounding debris must be cleared to ensure good ventilation and heat dissipation. This prevents debris from being sucked into the fan and damaging the impeller, or causing the motor temperature to rise due to poor heat dissipation.
The impeller dust should be cleaned once a month, especially for fans used in dusty environments. Dust accumulation can cause the impeller to become unbalanced and increase the starting load. When cleaning, the power should be cut off and the impeller should be fixed to prevent accidental rotation.
All inspection, start-up and fault handling situations must be recorded in detail, and the “Axial Fan Operation and Maintenance Record Form” should be filled out. The recorded content should include start-up time, parameter data, fault phenomena and handling results, and be archived for at least one year. For explosion-proof BT30 fans, additional attention should be paid: the junction box must be sealed properly, switches should be explosion-proof or installed in non-explosive areas to prevent electric sparks from causing danger.